AI patent application - knowledge extraction from patent documents with AI
Initial situation
Drafting an application text for a patent application is a complex process that is currently carried out by highly specialized experts on the basis of certain formal rules. The drafting of a new application text is usually based on existing patent documents. The patent attorneys at RACKETTE have been successfully supporting their clients for many years in the filing of new patents and in matters relating to patent law and therefore have extensive expertise in the drafting of new application texts.
Solution idea
The Quick Check examined approaches for extracting the knowledge of inventions dealt with in patent documents from the texts and making it available as structured knowledge graphs in order to make it easier to automatically compose texts for new applications in the future. Natural language processing (NLP) methods in the form of both rule-based procedures and unsupervised data-driven approaches were used for this purpose.
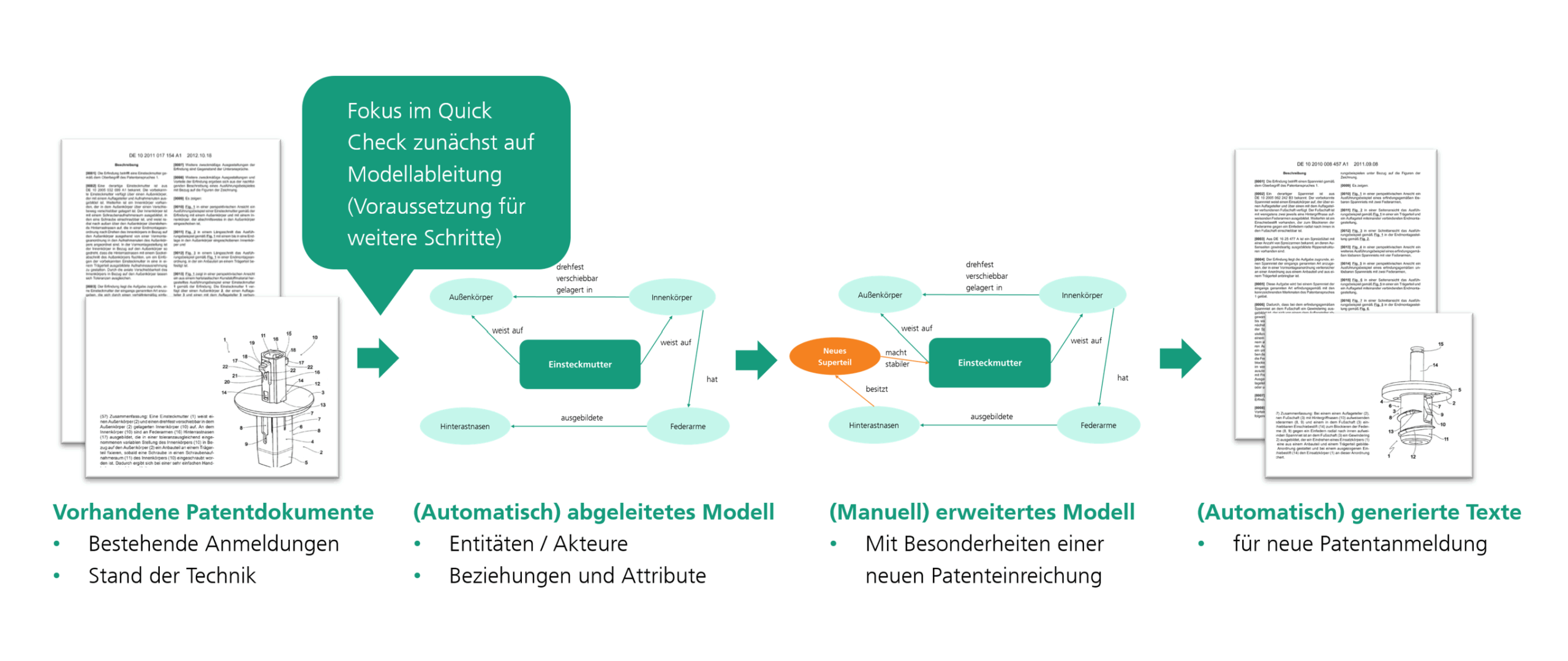
Benefit
The use of AI could enable RACKETTE to make the process of applying for new patents more efficient by saving a considerable amount of time in researching the state of the art and generating new text through (partial) automation. In general, all companies that deal with patent law can benefit from the use of AI: Even if current technologies do not yet enable fully automated generation of new applications, assistance functions that provide an overview of the principles covered in documents can offer considerable added value.
Implementation of the AI application
The prototype AI functions developed in Quickcheck enable the automatic extraction of structured information from the patent documents in the form of knowledge graphs with the most important entities and their relationships to each other. For this purpose, various rule-based methods were used to build graphs based on typical sentence constructions in the patent texts, as well as unsupervised matching algorithms that seek to determine applicable relationships between entities based on their occurrence in the sentence context through similarity matching.
